UV Exposure Across Surface of Earth
UV exposure across the surface of the earth is not a constant. It depends on the latitude (location on earths surface), the time of day, the time of year, the amount of cloud cover, the amount of pollution, moisture and the angle of the surface to the sun. Hence there are many variables to consider when considering the product design for outdoor exposure.
The Solar Constant
The Solar Constant is the amount of energy received at the top of the Earth's atmosphere on a surface oriented perpendicular to the Sun’s rays (at the mean distance of the Earth from the Sun). The generally accepted solar constant of 1368 W/m2 is a satellite measured yearly average. However, ongoing scientific measurements show that even this 'constant' is subject to some yearly variation due to earth sun distance and with variation in solar cycles. The Solar map below domonstrates how the average annual ground solar radiation varies across the surface of the earth.
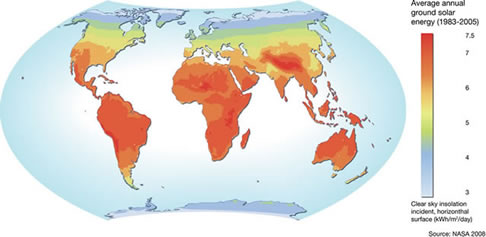
Therefore there can be a factor of 2 to 2.5 difference in total exposure between product exposed in a tropical region compared to that of temperature regions.
Insolation
In general, we are interested in the solar radiation that is received at the Earth's surface. Insolation is a measure of solar radiation energy received on a given surface area in a given time. It is commonly expressed as average irradiance in watts per square meter (W/m2) or kilowatt-hours per square meter per day (kW-h/(m2-day)).
The insolation on to a surface is largest when the surface directly faces the Sun i.e. is perpendicular to the suns rays. As the angle increases between the surface and the direction of the rays of sunlight, the insolation is reduced in proportion to the cosine of the angle.
Direct insolation is the solar irradiance measured at a given location on Earth with a surface element perpendicular to the Sun's rays, excluding diffuse insolation (the solar radiation that is scattered or reflected by atmospheric components in the sky). Direct Insolation or Normal Insolation is equal to the solar constant minus the atmospheric losses due to absorption and scattering. Whilst the solar constant varies with the Earth-Sun distance and solar cycles, the losses depend on the time of day (length of light's path through the atmosphere depending on the Solar elevation angle), cloud cover, moisture content, and other impurities.
Over the course of a year the average solar radiation arriving at the top of the Earth's atmosphere is roughly 1,368 watts per square meter. The Sun's rays are attenuated as they pass though the atmosphere, thus reducing the insolation at the Earth's surface to approximately 1,000 watts per square meter for a surface perpendicular to the Sun's rays at sea level on a clear day.
The actual figure varies with the Sun angle at different times of year, according to the distance the sunlight travels through the air, and depending on the extent of atmospheric haze and cloud cover. Ignoring clouds, the average insolation for the Earth is approximately 250 watts per square meter (6 (kW·h/m2)/day), taking into account the lower radiation intensity in early morning and evening, and its near-absence at night.
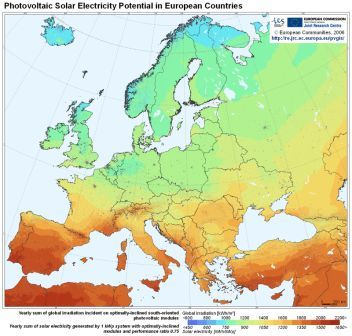
The solar map to the right shows a more detailed view of the European regions and demonstrates the differences in total irradiation between the UK and places like southern Spain.
We must remember that this radiant power is distributed across the entire electromagnetic spectrum, and most of the power is in the visible light portion of the spectrum. Approximately only 5% of this power is due to the UV light portion of the spectrum. Most testing machines will also control the sample irradiance at a given wavelength. Hence it is common to see figures of 0.76 - 0.83 W/m-2 at 340nm quoted as the standard sample test irradiance. This equates to the sea level, clear day, solar noon (noon day say) condition (i.e. when the sun is due south) and the sample is perpendicular to the suns rays i.e. an insolation value of 1000 watts per square meter.
